Intro
After initial installation, some examples are available to get familiar with the functionalities of the EVS, without the need for further configuration.
Functionality
General
The EVS allows a certain actor to perform, for a certain patient, a number of actions.
These actions are triggered by dropping input files in (subfolders of) the input-folder:
EVS watches these folder(s), executes the action(s) and generates output in the processed-folder:
Watching of these folders is done by the EVS application. The application can be launched via the "vault-uploader.cmd" batch file:
The behaviour of application must be determined by passing some mandatory parameters. Instead of using the "vault-uploader.cmd" batch file, it is easier to use the example batch file "start EVS.cmd":
Input-folder
Which patient?
The patient is determined by the folder under "..\exe\interaction\input".
After initial installation, 1 patient named "katrien" is available:
Which actor?
The actor is determined by the folder under "..\exe\interaction\input\<patient folder>".
After initial installation, 1 actor named "gp_van_gucht" is available:
Which files?
Any type of files, with any extension, can be dropped. They are considered as "input-files". EVS will, depending on the action folder, parse the files and extract the Kmehrmessage(s).
What is a Kmehrmessage?
A Kmehrmessage is that part of the file that starts with <kmehrmessage ...> and ends with </kmehrmessage>. One file can contain 0 or more Kmehrmessages.
EVS will only work with Kmehrmessages of Kmehr-standard 20120401. In this standard, 1 medicationschemeelement transaction and 0 or more treatmentsuspension transactions were considered as the business data of 1 "data entry".
All other data (among which the metadata) will be generated by the EVS and/or the Vitalink platform. As input the business data as depicted in blue here below will be used:
How is a Kmehrmessage identified?
For some actions, typically removing and updating data entries, the input Kmehrmessage need to have an identification.
There are 2 way to identify Kmehrmessages: by Vitalink ID and by EVS reference.
Identification by Vitalink ID
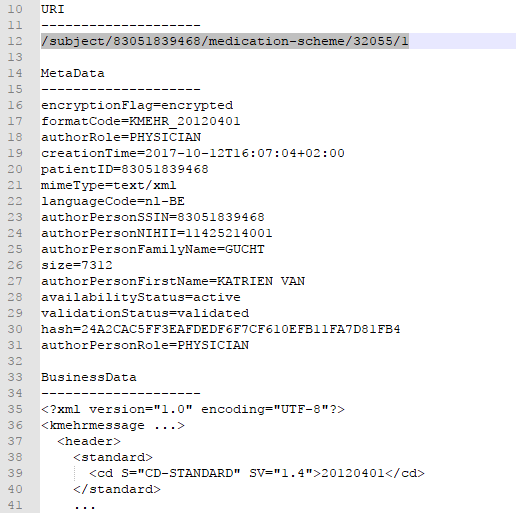
The Kmehrmessage can be preceeded by a Vitalink URI.
The Vitalink ID can not be chosen, but are dynamically generated by the Vitalink platform when adding new data entries. As a consequence, they are not deterministisc and are hard to use in when defining scenarios.
In the next example, this URI is /subject/83051839468/medication-scheme/32055/1. EVS detects the reserved format "/subject/###########/medication-scheme/32055" and finally uses "32055" as unique ID.
Identification by EVS reference
An EVS reference is put in 1 (and only 1) free text field in the concerned Kmehrmessage.
The EVS reference can be freely chosen, and support the definition and execurion of scenarios.
In the next example, this REF is "===EVSREF:901===". EVS detects the reserved format "===EVSREF:###===" and finally uses "901" as unique REF.
Which actions?
Depending on the folder where the inout-file is dropped, EVS will execute an action.
Action "add"
This action will add a data entry to the vault for each Kmehrmessage found in all dropped files.
In the example below, 3 Kmehrmessages are dropped to be added to the vault:
Action "empty"
This action will remove all data entries from the vault. EVS will do this action once for each dropped file, without any parsing.
In the example below, a newly created file will trigger emptying of the vault by removing all existing data entries:
Action "export"
This action will export the contents of the vault, without any change to the vault itself. EVS will do this action once for each dropped file, without any parsing. .
In the example below, a newly created file will trigger exporting the contents of the vault by removing all existing data entries:
Action "removeID"
This action will remove the data entries identified by the Vitalink ID in the input file from the vault.
Action "removeREF"
This action will remove the data entries identified by the EVS REF in the input file from the vault.
Action "replace"
This action will replace the contents of the vault by all the Kmehrmessages found in the input file. Be aware of the fact the dropping multiple files in the replace-folder will result in a vault with as contents the Kmehrmessages of the last input file!
In the next example, after processing the next 3 input files, the vault contains 2 data entries.
Action "updateID"
This action will update the data entries identified by the Vitalink ID in the input file.
Action "updateREF"
This action will update the data entries identified by the EVS REF in the input file.
Processed-folder
Each action
Configuration
This paragraph explains how to configure the EVS for your own needs.
How to add an extra patient?
Extra patients can be added by creating files in the next folder:
After initial installation, 2 patient config files are already present. Both can be used as example (copy-paste) to add extra patients. The name of the file, without the extension, needs to be used to identify for which patient the action needs to performed.
After copy paste of the example files, insert the correct info for the new patient:
Off course, since EVS follows all the rules for eHealth and Vitalink, it is up to the user to make sure the proper eHealth dependencies (informed consent, therapeutic relation, ...) are set in function of the wanted behaviour.
How to add an extra actor?
Extra actors can be added by creating files in the next folder:
After initial installation, some actor config files are already present. All can be used as example (copy-paste) to add extra actors. The name of the file, without the extension, needs to be used to identify for which patient the action needs to be performed.
The template examples are given for 3 different types of actors: doctor, nurse and pharmacy.
Off course, since EVS follows all the rules for eHealth and Vitalink, it is up to the user to make sure the proper eHealth dependencies (informed consent, therapeutic relation, ...) are set in function of the wanted behaviour.
Appendix A: Folder structure EVS 1.x.y
This paragraph gives a brief overview of the folder structure after initial installation. It can be used as reference while using and configuring the EVS.
| Path | Reserved path | Reserved name | Explanation | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
<zip folder> default=EVS+version | \<root folder> default=EVS | \config | Everything that defines the behaviour of the EVS, configured as needed by the user. | |||||||
| \actors | ||||||||||
| \log4j | ||||||||||
| \patients | ||||||||||
| \exe | ||||||||||
| \certificates | ||||||||||
| \exports | ||||||||||
| \interaction | ||||||||||
| \input | ||||||||||
| \katrien | ||||||||||
| \gp_van_gucht | ||||||||||
| \add | ||||||||||
| \empty | ||||||||||
| \export | ||||||||||
| \removeID | ||||||||||
| \removeREF | ||||||||||
| \replace | ||||||||||
| \updateID | ||||||||||
| \updateREF | ||||||||||
| \patient_template | ||||||||||
| \processed | ||||||||||
\scenarios | ||||||||||
| \basic_example | ||||||||||
| \system | ||||||||||
| \dependency-jars | ||||||||||
Identification by Vitalink ID